As electric vehicles (EVs) and electric boats expand globally, charging connectors vary by region, power level, and application. Understanding these standards is essential for vehicle compatibility, infrastructure planning, and battery system design.
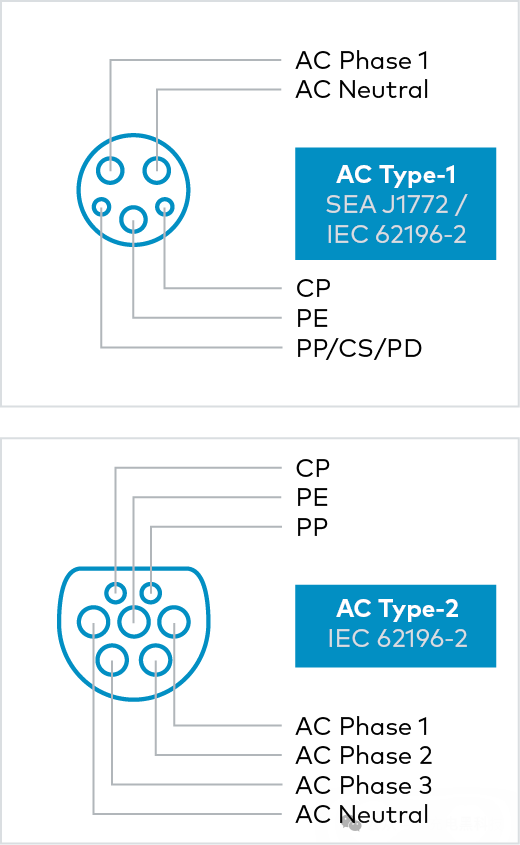
AC Charging Interface
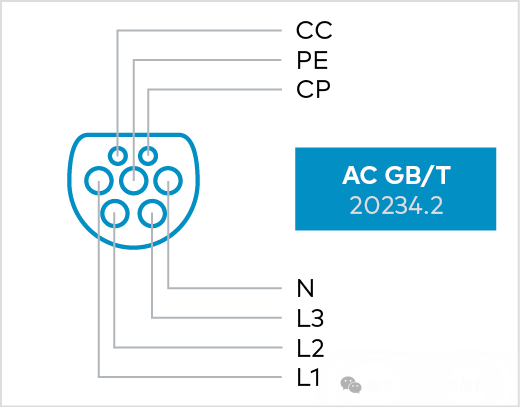
GB/T 20234.2 supports both single-phase and three-phase charging in charging mode 3. The GB/T charging cable uses identical male connectors at both ends, similar to those used in Type 2 connectors.
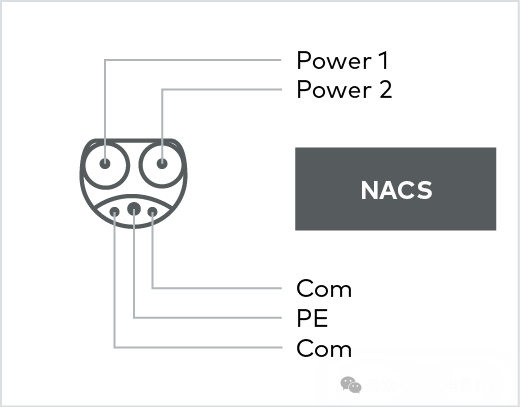
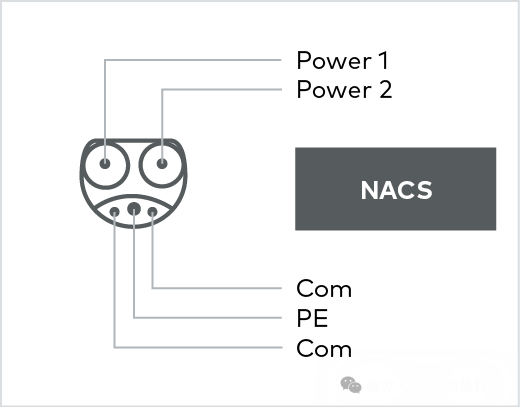
NACS uses connectors that are compatible with Tesla's design and protocols. In addition, it also supports the IEC 61851 AC charging standard.
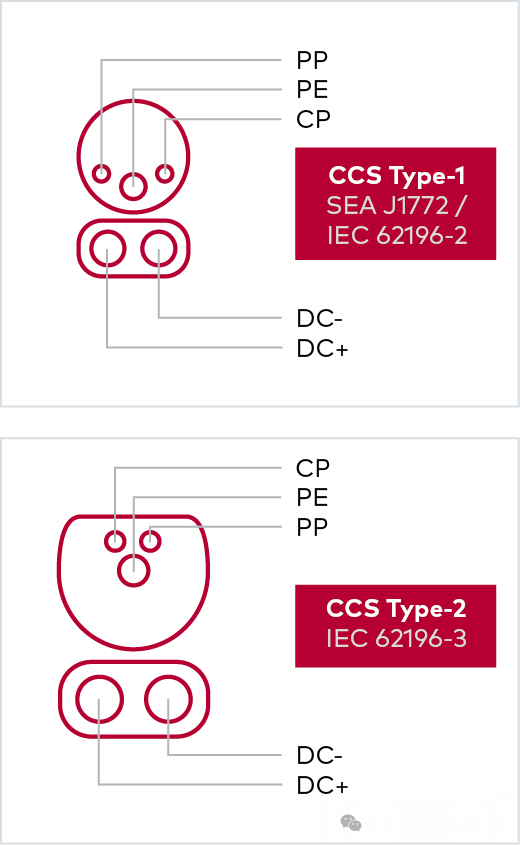
DC Charging Interface
CCS1 CCS2
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is an extension of AC Type-1 and Type-2 connectors, designed to achieve high DC charging capacity, and includes two additional high-power contacts. Like AC charging, CCS also uses CP, PP, and PE pins, and extends the connector with positive and negative contacts. To enable advanced communication for smart charging, Power Line Communication (PLC) functionality is superimposed on the CP pin.
Pin description: CP: Used for communication between the electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) and the electric vehicle (EV) (control signal exchange). The EVSE provides a ±12V 1kHz square wave signal between the CP and PE lines, and the EV can control charging by modulating the amplitude of this signal (PWM communication). CP also has a safety function; if the CP connection is interrupted, the charging process will be terminated.
PP: Used to prevent the electric vehicle from moving while connected to the charging station. The electric vehicle can only move after the charging plug is disconnected. In Type 2 connectors, the PP pin is also used to detect the current load capacity of the charging cable. In Type 1 connectors, this pin is used for manually unlocking the plug.
The Japanese DC charging standard is based on the CAN bus and is used exclusively in Japan, although some export electric vehicles from Mitsubishi, Nissan, and Renault have recently adopted this standard as well.
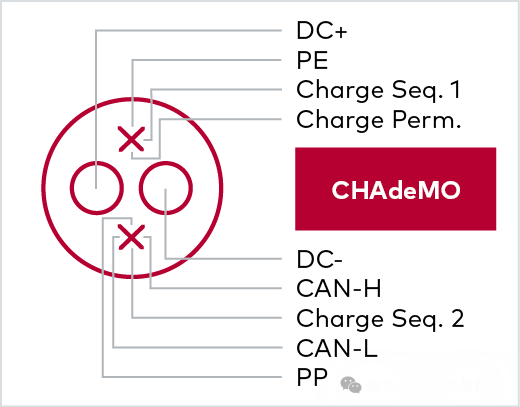
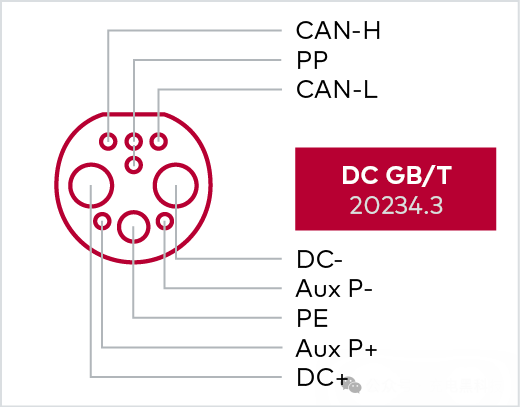
It provides charging power of up to 900 kW.

The MCS is designed specifically for DC charging in the 3.75 MW range and is suitable for large battery electric vehicles such as heavy-duty vehicles. It features two communication lines independent of CE (Charge Enable) and ID (Insertion Detection). Its communication method and basic principles are based on the ISO 15118-20 standard, but it uses a different connector. The underlying communication of the MCS follows the IEC 61851-23-3 standard, while its higher-level communication follows the ISO 15118-20 standard.
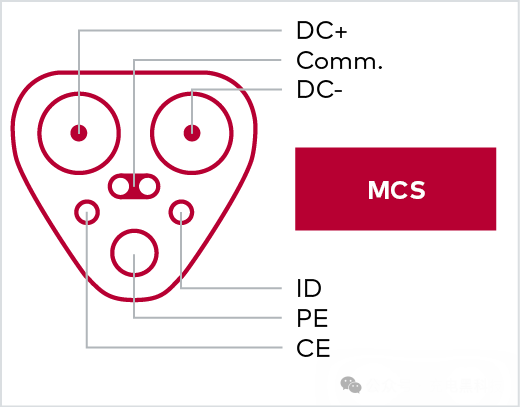
It uses connectors compatible with Tesla and supports multiple communication protocols.
 Hot News
Hot News2024-09-18
2024-12-25
2025-01-15
2025-09-30
2025-10-28
2025-10-30